What is the difference between pickling and passivation? Stainless steel castings will have a black scale during processing. In order to improve the appearance and corrosion resistance, the processed stainless steel parts need to be pickled and passivated surface treatment!
During the processing of stainless steel castings, pickling and passivation is generally carried out at the same time. Pickling is to remove rust and scale on the surface of stainless steel. Passivation is the formation of a passive film on the surface of stainless steel. In rust-free and clean condition. Protect the surface of stainless steel from corrosion.
Pickling can remove the oxide layer on the surface of the workpiece. Passivation is the formation of a new chromium-rich protective layer on the surface of the workpiece. If it is not treated after pickling, it tends to be more prone to rust. After passivation, the anti-oxidation ability can be greatly improved.
What Is Pickling?
Pickling is a metal finishing process that used to remove impurities. Such as rust, scale, and oxide layers, from the surface of a metal. It is commonly used on steel and other ferrous metals. The process involves immersing the metal in an acidic solution. And hydrochloric acid, which reacts with the impurities and dissolves them away. Done before other metal finishing processes such as painting or plating. The process is usually carried out at high temperatures. And for a specific duration in order to achieve the desired results.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pickling
Advantages of Pickling:
- Removes impurities
- Improves adhesion
- Enhances appearance
- Increases corrosion resistance
- Cost-effective
Disadvantages of Pickling:
- Environmental concerns
- Health hazards
- Risk of damage
- Time-consuming
- Limited application
What Is Passivation?
Passivation is a metal finishing process. Used to protect the surface of metal from corrosion. It is primarily used on stainless steel and other metals that contain a high amount of chromium. The process involves immersing the metal in a solution of an acid. Such as nitric acid, that reacts with the surface of the metal to form an oxide layer. This oxide layer acts as a barrier to protect the metal from corrosion. Passivation is done after other metal finishing processes. Such as welding or polishing, too restore the corrosion resistance of the metal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Passivation
Passivation is a metal finishing process. Used to protect the surface of metal from corrosion. It creates a passive oxide layer on the surface of the metal. That acts as a barrier to protect the metal from corrosion. Passivation has many advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Passivation:
- Protects against corrosion
- Improves surface finish
- Enhances resistance to wear and tear
- Cost-effective
- Suitable for a wide range of metals
Disadvantages of Passivation:
- Risk of damage
- Environmental concerns
- Limited effectiveness
- Time-consuming
- Requires specific conditions
What is the difference between pickling and passivation?
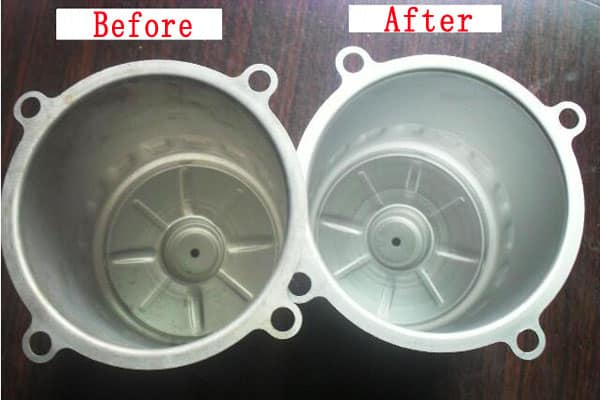

Different in nature
1. Pickling: Use an acid solution to remove oxides and rust on the surface of steel or castings. It is a method of cleaning metal surfaces.
2. Passivation: The metal is oxidized by a strong oxidant or electrochemical method. Making the surface an inactive state. That is the process of passivation state.
Principle is different
1. Pickling: Generally, the workpiece is immersed in an aqueous solution. Such as methionine to remove oxide and other films on the metal surface. It is the pretreatment or intermediate treatment of electroplating, enamel, rolling, and other processes.
2. Passivation: If the corrosion product produced by the metal under the action of the medium has a dense structure, a thin film (usually invisible) is formed. Tightly covering the metal surface will change the corrosion performance of the metal. The surface state of the metal makes the electrode potential of the metal jump to the positive direction. Becomes a corrosion-resistant passivation state.
The process is different
1. Pickling: hang stainless steel parts → chemical degreasing (conventional alkaline chemical degreasing or surfactant degreasing) → hot water washing → running water washing → first pickling → running water washing → second pickling → water washing → The next process (such as chemical coloring)→recycling→water washing→hardening treatment→water washing→sealing treatment→water washing→drying→finished product)
2. Passivation: Before pickling and passivation of stainless steel workpieces, if there is surface dirt, it should be cleaned mechanically. Then skim. If the pickling passivation solution cannot remove grease. The presence of surface grease will affect the quality of pickling passivation. For this reason, degreasing cannot be omitted. It can be cleaned with lye, emulsifier, and steam.
Stainless steel pickling passivation method:
According to the material of stainless steel and the severity of oxidation, it can be used as a stock solution. Or it can be diluted with water at a ratio of 1:1~4. Ferritic, martensitic and austenitic stainless steels with low nickel content. Such as 420, 430, 200, 201, 202, 300, 301, etc. are used after dilution.
Austenitic stainless steel with high nickel content (such as 304, 321, 316, 316L, etc.) is immersed in the stock solution. It is generally used at room temperature or heated to 50-60 degrees. Soak for 3-20 minutes or longer (the specific time and temperature are determined by the user according to their own trial conditions). until the surface dirt is completely removed. Until a uniform silver-white dense passivation film is formed. After processing, take it out, rinse it with clean water, and let it dry. Rinse with alkaline water or lime water for neutralization.
Stainless steel pickling passivation is generally treated with pickling passivation paste and pickling passivation solution. The pickling passivation paste is pickling and passivation at the same time. This changes the traditional pickling and passivation process.
The operation is simple, the construction is convenient, and the cost is low. Suitable for large-area painting operations. The pickling passivation solution is suitable for the immersion of small workpieces.